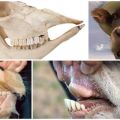
The number of teeth in a ram and the structure of the jaw, how to determine age by them
The first domesticated animal, along with the wolf, is the sheep. The ability to eat tough and withered grass, to which the teeth of sheep and rams are adapted, helped the first people to move from a nomadic life in pastures to a sedentary one. During this time, a huge experience has been accumulated in the maintenance and breeding of such an unpretentious animal. An important issue remained to study the structure of the teeth, which are not only an indicator of health, but also the age of the sheep.
Teeth structure in sheep
The teeth of a ram, like all cloven-hoofed animals, are a noticeable part protruding from the gums. They consist of a crown, neck, root. The latter is immersed in the alveolar bone, which fixes it. Usually 6-10 mm long. The neck from the root to the crown is less pronounced. The front incisors are in the shape of an elongated triangle.
Tooth components:
- The pulp is the central tissue in which nerve connections and blood vessels are concentrated.
- Dentin - surrounds the pulp, base, core.
- Enamel is the outer fabric, the strongest part, which receives the greatest stress during chewing, therefore it is subject to destruction.
Enamel is the hardest of all tissues in the body of an animal. The film that forms on the surface of the tooth, protecting it from acid attack, disappears during grinding of food.
Types and their number of teeth
The ram chews the grass with thirty-two teeth (tooth formula I: 0/3 C: 0/1 P: 3/3 M: 3/3). Of these: 8 anterior incisors and 24 molars. The incisors are located only in the lower part of the jaw, and at the top is the hard palatine plate. The long incisors are angled to provide the lowest possible grip on the grass (unlike other ruminants).
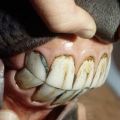
Interestingly, in the German city of Bonn, sheep are used instead of lawn mowers, so perfectly they pull out the grass. It is more convenient for sheep to chew grass with the wide surface of the back of the jaw, consisting of false-rooted teeth (premolars) and real molars, or molars. The central pair of incisors in the lower jaw are called hooks. The adjoining pair is medium, followed by the corner ones, and the edges close the row. There is a difference between incisors of the same row, or arcade. The volume, height of the arcade decreases from hooks to edges. A long gap that is not covered with teeth from the margins to the premolars is called the edentulous margin.
Teething, changing, erasing
As a rule, lambs are born without teeth, but some appear with one, sometimes three pairs of incisors. According to statistics, the hooks erupt after a week of the sheep's life. After a month, the lambs are gradually transferred to hay. Solid food grinds down milk teeth, speeding up their replacement. Permanent incisors differ significantly from milk ones in volume and size. But the three back molars remain unchanged.
Determining the age of an animal by teeth
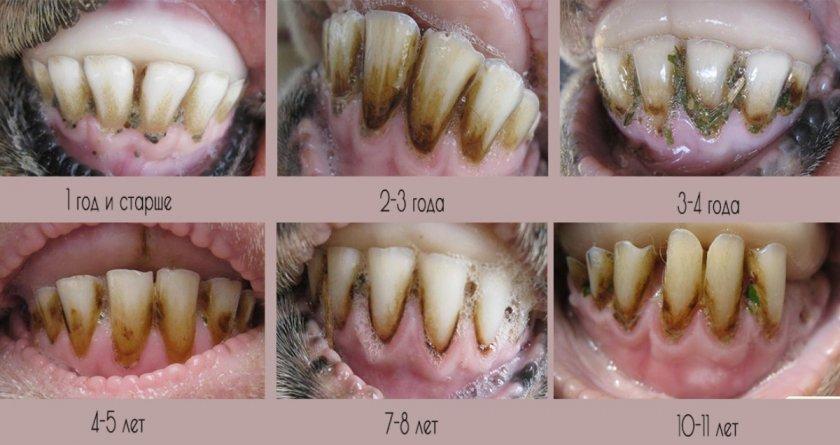
The ears of animals are marked from the moment of birth, but if the tag is lost, the age can be determined by the dental jaw. The criteria are the shape and order of the molars and incisors.
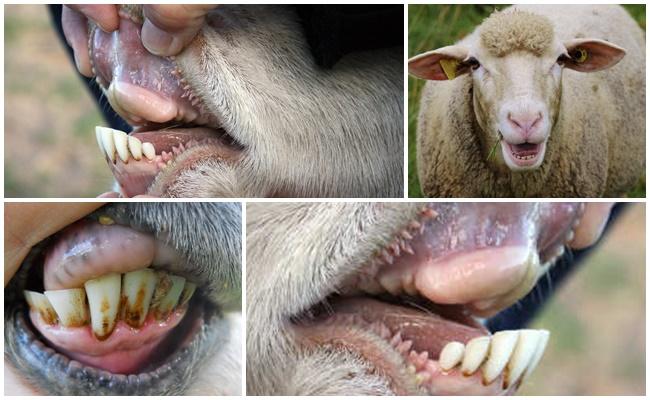
At 4 years old, the arcade update ends. It is dense, even, well closed. The toes are wide, without signs of wear. By the age of five, the enamel becomes thinner, gaps appear. At 6-7 years of age, the slots become wider, the incisors take the shape of a chisel. At 7-8 years of age, tooth loss begins.
Determining the age of an animal is not difficult, it is important to consider the following points:
- what kind of jaw does it look like (milk or permanent);
- how much;
- condition (erased or even, how they close, their length, the presence of cracks);
- what color (milky white or yellow);
- take into account individual characteristics (breed, food, conditions of detention).
The sequence of the period of tooth growth is as follows:
| Age | Growth stages |
| 5-12 days | hooks are cut |
| 9-14 days | 4 incisors grow (middle and outer) |
| 2 months | the edges come out, the length of the arcade of the incisors is not the same |
| 3 months | 1st molar appears (milk) |
| 9 months | the 2nd molar is visible below |
| up to 1 year | a complete change of middle and internal incisors |
| after a year, up to one and a half years | the process of replacing the hooks with permanent |
| 18 months | the 3rd molar erupts, the edges of the permanent hooks are erased |
| 24 months | the 1st premolar of the lower jaw is clearly visible, the incisors, molars are aligned under one line |
| 2 years 5 months | traces of erasure of internal crowns are poorly visible |
| up to 3 years | all external incisors change |
| 3 years 5 months | complete replacement of all dairy |
| 4 years | arcade levels |
| 4 years 5 months | chewing grinds off the edges |
| 5-6 years old | abrasions are visible, roots protrude from the gums |
| 6-7 years old | the holds become thinner, gaps are noticeable. The roots are mobile, turn yellow, begin to fall out, the shape changes to a quadrangular |
Important! Proper nutrition helps the sheep to keep their teeth healthy and intact, therefore, culling occurs later.
When sheep are culled in old age
On average, rams live up to 15 years. If a sheep loses its teeth, it means that it will not be able to eat properly. No matter how old she is, it is not profitable for the farmer to maintain her. It is required to examine every animal that has reached a critical age, and personally decide whether to cull or leave it on soft feed.
Teeth and feed quality
From 5 months, the quality of the feed begins to influence the degree of wear on the jaw. Grazing on old, hardened grass accelerates the wear of the holds. Juicy greens are more suitable for the tender age of lambs. If the diet of rams contains mainly roughage, the incisors are shortened too quickly, which can reach the gums.
Lack of friction, on the contrary, promotes an increase in the lateral incisors, which injure the oral cavity. Another reason for abrasion is warm swill - by the age of 6, sheep can lose some of their teeth.
It is interesting! Despite the harsh living conditions, bighorn sheep live up to 24 years.