Symptoms and treatment of acidosis in cows, causes and consequences for cattle
Acidosis is a disease that develops in cattle due to excessive production of lactic acid in the rumen. In the body, the acid-base balance shifts, the animal loses its appetite, becomes lethargic. It is imperative for the farmer to be aware of the causes of rumen acidosis in cows, the symptoms and treatment options in order to prevent possible complications in time. A large amount of roughage should be present in the diet of cattle to prevent acidosis.
Features of the disease
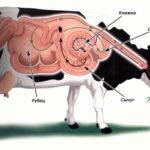
Rumen acidosis is a very common pathology among cattle, which occurs when the rules of animal feeding are not followed. The increase in the number of cases of acidosis is attributed to the widespread use of concentrated silage rations by farmers.
In the diet of cattle, roughage (hay, straw with long-fiber fiber) must be present. When acidic, wet feed, low-quality hay and silage are used, the pH level in the rumen decreases (to 5.2-5.5), as a result of which milk yield falls, milk quality deteriorates, and cattle are prematurely culling.
A high amount of butyric acid in the silage builds up when wet or contaminated grass is dominant. Protein breakdown occurs, cows receive less energy, lactic acid prevails in the rumen, and the volume of rumen contents decreases.
The harmful substances released during the death of bacteria are carried through the blood to the internal organs, causing inflammatory processes. Due to a sharp drop in blood glucose levels, fatty liver syndrome and ketosis (the result of the extraction of glucose from fat stores) can develop. In chronic acidosis, inflammation of the tissues under the hoof horn occurs - laminitis.

Causes of acidosis in cattle
Rumen acidosis develops in cattle for the following reasons:
- excess of sugar and starch in feed;
- the use of finely ground feed - leads to a reduction in the time of chewing food and a decrease in the pH level;
- increased feed moisture - causes a decrease in the duration and activity of chewing gum;
- the use of too acidic feed and concentrates - in particular, silage, which contains more than 2.5% acids;
- a sharp change in the fodder menu - no smooth transition when opening a new trench for haylage and silage (less than 1-1.5 weeks);
- poor quality feed;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals - a lack of calcium, phosphorus, cobalt, selenium, magnesium, iodine, vitamins of groups A, D, E leads to the death of beneficial microflora and deterioration of food digestion.
In order to avoid the development of acidosis, it is not recommended to quickly transfer cows from the diet of dry animals to the milk menu, which includes a large volume of concentrates, to introduce an excess of sour bagasse, stillage, molasses, wheat grains and barley into the menu.
The main symptoms and forms of pathology
Most often, signs of acidosis develop in cows with improper preparation of farmers for calving animals - a sharp transition to a post-calving diet, an increased content of sugar and starch in feed, a deficiency of structural fiber.
Acute degree
The acute form of acidosis develops with a rapid and sharp increase in the volume of concentrates in the cow menu. If animals consume a lot of easily digestible carbohydrates, the level of lactic acid in the rumen rises significantly, and the pH values fall below 6. It is manifested by pronounced symptoms:
- prolonged diarrhea;
- the risk of developing dehydration;
- necrotization of cicatricial microflora with the danger of internal poisoning.
Acute acidosis is easy to diagnose and quicker to treat.

Subacid (subacute)
The subacute form of acidosis is most dangerous for cows, because it manifests itself in too weak signs that inattentive farmers may not notice for a long time:
- lethargy;
- increased feeling of thirst;
- covering the tongue with a coating;
- periodic episodes of bloating;
- general body temperature is within normal limits.
As a result of the prolonged course of subacute acidosis, the cow may develop such complications as anorexia, scar atony, respiratory and heart rhythm disturbances.
Permanent (chronic)
The chronic form of rumen acidosis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- indifferent behavior of the cow, lack of response to stimuli;
- malnutrition of feed or complete refusal to eat;
- weakening of the motility of the scar;
- anemia of the mucous membranes;
- bouts of diarrhea;
- reducing the volume of milked milk, lowering the fat content;
- low pH in the rumen.
If treatment is not taken for a long time, chronic acidosis leads to kidney damage, the formation of an abscess in the liver, laminitis, ruminitis, damage and degeneration of the heart muscle.
Diagnostic methods
To diagnose rumen acidosis, it is necessary to measure the pH level in one of the following ways:
- take away part of the feed from the cow's mouth while chewing gum - the method is not considered reliable, since the rumen contains a certain amount of saliva;
- using a probe;
- make a puncture in the rumen to take its liquid contents for analysis.
The veterinarian must not only detect symptoms of acidosis, but also confirm the diagnosis. In the chronic form of the disease, the shift in the acid-base balance is manifested in the region of 5.2-5.6 for at least three hours a day.
How to cure the problem
In the acute form of acidosis, treatment should be started immediately, since within 1-2 days a serious illness can end fatally, the risk of developing laminitis, myocardial dystrophy and liver abscess is high.

Veterinary care
Treat acute acidosis by washing the scar with a gastric tube. To quickly restore the impaired functions of the proventriculus, about three liters of rumen fluid taken from healthy animals are injected into the rumen.
To normalize pH values, sodium bicarbonate (at a concentration of 4%), Ringer-Locke solutions, Trisol up to 800-1000 milliliters are injected intravenously. Baking soda is diluted and given to a sick animal to drink 7-8 times a day (150 grams of soda per 1 liter of water).
Method of treatment from V.A.Lochkareva - with the help of a trocar sleeve, inject a solution of potassium permanganate in a volume of 3 liters into the accessible layers of the scar, then 2.5 liters of an 8% sodium bicarbonate solution. The introduction of solutions is performed at intervals of 4 hours until the condition of the cow improves. After the trocar sleeve is removed, and the puncture area is treated with "Tricillin".
Folk remedies
With the help of folk remedies, you can help the cow before the arrival of the doctor in order to alleviate the well-being of the animal. It is useful to give her a solution of baking soda to drink (100 grams per 3 liters of water at room temperature). Immediately after the soda solution, the animal needs to drink 1 liter of vegetable oil. After the manipulations, in order to start the digestive function, it is necessary to massage the scar.
Prevention of acidosis
To prevent acidosis, it is important to follow the rules for feeding cattle:
- introduce no more than 40-45% of concentrates into the diet of cows;
- provide cattle with at least 16% fiber per day;
- feed at least 2.5 kilograms of hay or straw per head daily;
- do not exceed the amount of easily digestible carbohydrates in the menu - up to 26% starch, up to 7% sugar;
- do not give feed mixtures with moisture above 60%;
- transfer animals from one type of food to another gradually (within 2-4 weeks);
- to provide cattle with grain fodder from cereals and legumes;
- introduce feed yeast into the diet.
In the summertime, it is recommended to graze dry animals on pasture to normalize the digestive function, metabolic processes, and improve immunity. It is important to monitor the quality of compound feed - they must be fresh, dried, not include elements of rot or mold.
The key to good digestion in cattle is proper feeding. To prevent rumen atony and change the pH level, it is useful for cows to give enzyme preparations, mixing them with compound feed (the dosage and duration of use is determined by the veterinarian). Periodically, baking soda solution can be given to the cattle to reduce the amount of acid in the rumen.